| Unit 20 | Paper and Pulp |
|---|---|
| 20.1 | Introduction |
| 20.2 | Raw materials |
| 20.3 | Sources of raw materials |
| 20.4 | Stages in production of paper |
| 20.5 | Flow-sheet diagram for paper production |
| 20.6 | Quality of paper |
Applied Chemistry Unit 20: Paper and Pulp
In today’s world, paper is essential material for human being. It is used for book, writing, newsprint, packaging, tissue etc. Formation of paper involves mainly two steps:
- Pulping
- Paper making
Pulp: Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared chemically or mechanically by separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops, waste paper or rags.
Paper: Paper is the aqueous deposit of any cellulose fibre (wood, fibre crops) in sheet form. Generally, bamboo, straw, jute, waste paper etc. are used to make paper.
Historically, the first paper-like plant-based writing sheet was called Papyrus found in Egypt (4th century) but the first true paper was documented in China during Eastern Han Period.
RAW MATERIALS FOR PAPER INDUSTRY
Raw materials for paper making include synthetic, mineral or plant fibres. Most of the paper is manufactured using pulp from wood.
The raw materials which are used to prepare paper is pulp. The materials used to prepare pulp are:
- Fibrous raw materials
- Non-Fibrous raw materials
1. Fibrous raw materials
- Conventional material type: bamboo, Wood, etc.
- Soft wood: Coniferous and non-coniferous wood e.g. pines.
- Hard woods: Eucalyptus, mulberry, rubber plant wood etc.
- Non-Conventional material type: rice straw, wheat straw, etc.
- Waste product type: sugar bagasse, Sawdust, etc
- Cotton type: cotton, cotton rags, jute, etc.
- Grass and reeds: a tall plant with hollow stem e.g. Lemon, bamboo etc.
2. Non-Fibrous raw materials
- Inorganic raw materials: Na2S, NaOH, TiO2, etc.
- Organic raw materials: Wax, glycerols, glue, etc.
Sources of Raw materials
A major source of pulp is woods. The sources of Raw materials used in paper production classified as:
- Wood Type: Hard wood like gum, paper mulberry, rubber plants etc & Soft wood like pine, fir, etc.
- Grass Type: Lemon grass, reeds, siru, babiyo, kush, etc
- Straw Type: It is based on rice, wheat, barley, etc.
- Waste product: This includes bagasse, sawdust, etc.
- Recycling materials: Various types of waste paper can be recycled for the preparation of paper.
Read more: Cement Notes | Class 12 Chemistry
STAGES IN PRODUCTION OF PAPER
The main stages in production of paper are
- Raw material preparation and handling
- Preparation of fiber suspension ( pulp manufacturing)
- Bleaching process
- Paper making procedure
The general paper production can be explained details in the following steps:
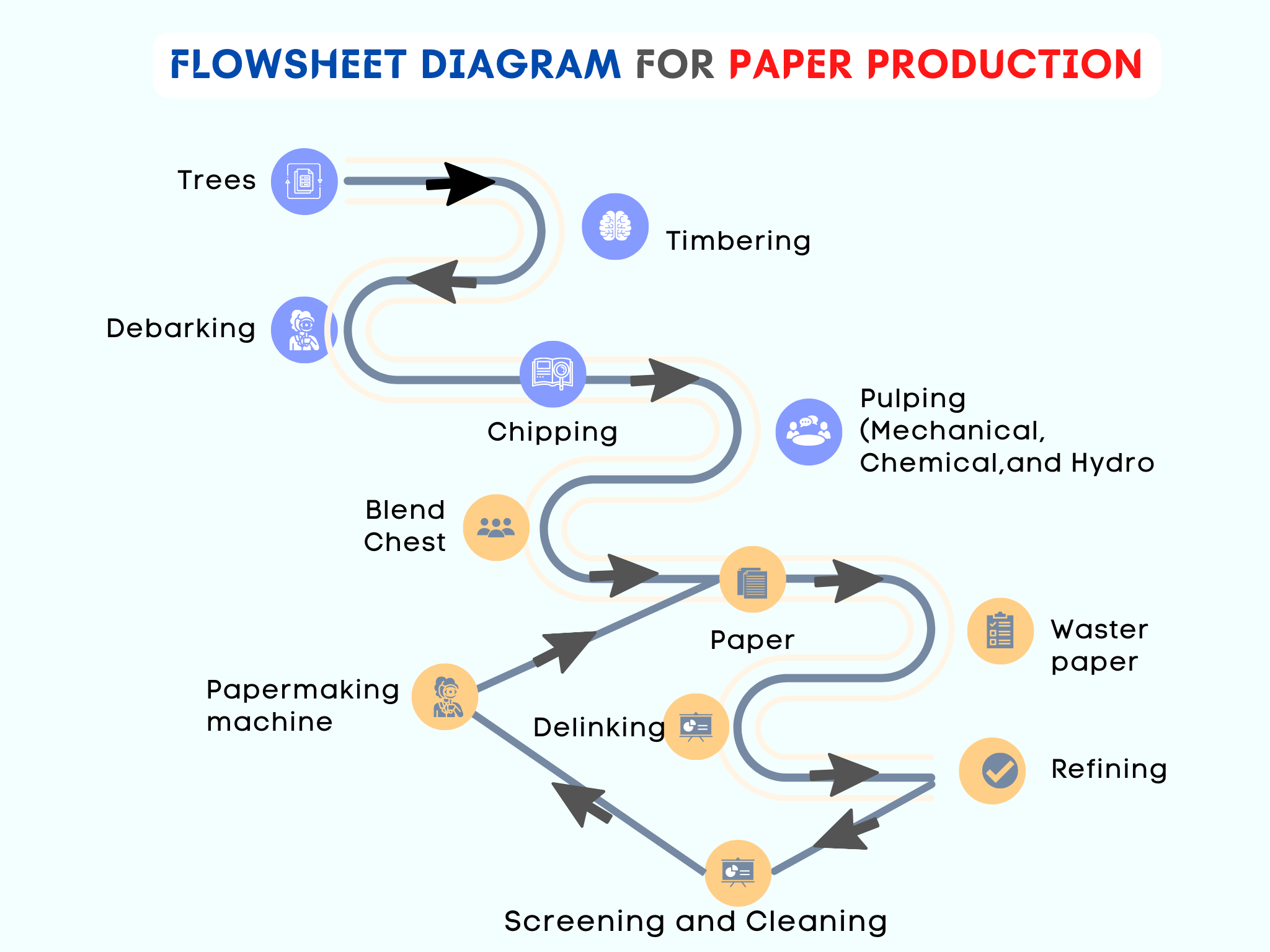
1. Timbering
Timbers are obtained from mature trees. The quality of paper depends upon the quality of timber.
2. De-barking
It is the process of removing the bark of trees. This process is performed hydraulically with a high-pressure jet or mechanically by rubbing logs. Stripped timber is used for paper production.
3. Chipping Process
Stripped timbers are chipped into small pieces using a rotatory disc and heavy knives. The chips are then digested in a digestor tower where maximum lignins are removed with minimum loss of cellulose.
4. Pulping
The disintegration of long and bulky fibrous materials into individual or small bulky mass is called pulping. There is mechanical, Chemical and Hydropulping method to produce pulp.
It is the process by which the bond within the wood structure is ruptured either mechanically or chemically.
- Mechanical pulping process: Here, rotatory steel discs with teeth are used to tear wood parts.
- Chemical pulping process: Here, wood chips are fed into a digestor and cookedto remove lignin. Here, chlorine, Sodium hypochlorite are used.
- Hydropulping: Here, wood fibres are brought into a circular tank with a powerful agitator containing a water supply that breaks the wooden fibres into small pieces.
5. Blend Chest
Chemicals are added to obtain desired features of the paper. In some cases dyes can be used to obtain the color of paper.
6. Waste Paper Collect
Waste papers collected from commercial dumps are included here.
7. De-inking
Here, the inks are removed from waste papers by washing.
8. Refining
Cellulose fibres are stiff and inflexible. So, these cellulose fibres are refined to avoid these unwanted properties.
9. Screening and Cleaning
Processed pulp may contain undesirable fibrous and non-fibrous material which should be cleaned. Centrifugal cleaners are employed here.
10. Conversion and Printing
The slurry of fibres is drained to prepare a continuous paper web which is passed through a pressing section to squeeze out excess water and dried.
FLOWSHEET DIAGRAM FOR PAPER PRODUCTION
The flowsheet for paper production is given as:
QUALITY OF PAPER
The quality of paper is determined based on the following characteristics:
- Brightness: It means the percentage of light that paper reflects. Generally, coated papers have a better appearance than uncoated paper.
- Colour
- Finish: It includes the characteristics of the surface of the paper.
- Sizing: It must be uniform so that when ink is applied, the lines appear clean.
- Opacity: It is related to the thickness of the paper.
- Clarity
- Weight: The weight of paper is explained based on Grammage and is defined as the weight per square metre and expressed in gsm. Grammage up to 200 gsm are considered as paper whereas above 200 gsm are considered as paper board or low-quality board.
ENVIRONMENTAL IMPACTS OF PULP & PAPER INDUSTRIES
Paper manufacturing has used up about 40% of all global wood, 4% of the world’s energy. The wastes released from paper and pulp industries like oxides of nitrogen, sulphur, carbon, chlorine-based bleaching agent contribute a lot to environmental pollution.
PULP AND PAPER INDUSTRIES IN NEPAL
4 decades of production of paper & pulp has been recorded in context to Nepal. According to recent data; 46 paper & pulp industries are in operation at present. Everest Paper Mills Pvt.
Ltd. (1982, Janakpur) is the first paper manufacturing industry in Nepal. Bhrikuti Pulp and Paper Nepal Limited (1985) was the 1st state-owned paper industry later was permanently closed in 2011.
LOKTA PAPER
- Nepali handmade paper made up of fibrous inner bark of high elevation evergreen shrubs namely Daphne bholua and Daphne papyracea.
- Durability and resistance to tearing, humidity, insects have made lokta paper to be used widely in the Nepali legal sector as Nepali Kagaj (नेपाली कागज).
Differences Between
The difference between Sulphite Pulping process and Kraft Pulping process (Sulphate process) is given as:
| Sulphite Pulping Process | Kraft Pulping Process OR Sulphate Process |
|---|---|
| It is a technique used to produce wood pulp using sulphites or bisulphite salt of sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium and ammonium. | It is a technique used to convert wood into wood pulp using a mixture of water, sodium hydroxide, sodium sulphide. |
| It produces stronger cellulose fibres. | It produces weak cellulose fibres. |
| Its efficiency is high. | Its efficiency is low. |
| It causes less harm to the environment. | It causes more harm to the environment. |
Read more: